Many people consider varicose veins to be a cosmetic problem. Spider veins or protruding veins give the legs an unsightly appearance, but they also warn of more serious health problems. Noticing the signs of varicose veins in time, carrying out treatments and preventing relapses are the main tasks of those who want to maintain their health and preserve the beauty of their legs for as long as possible.
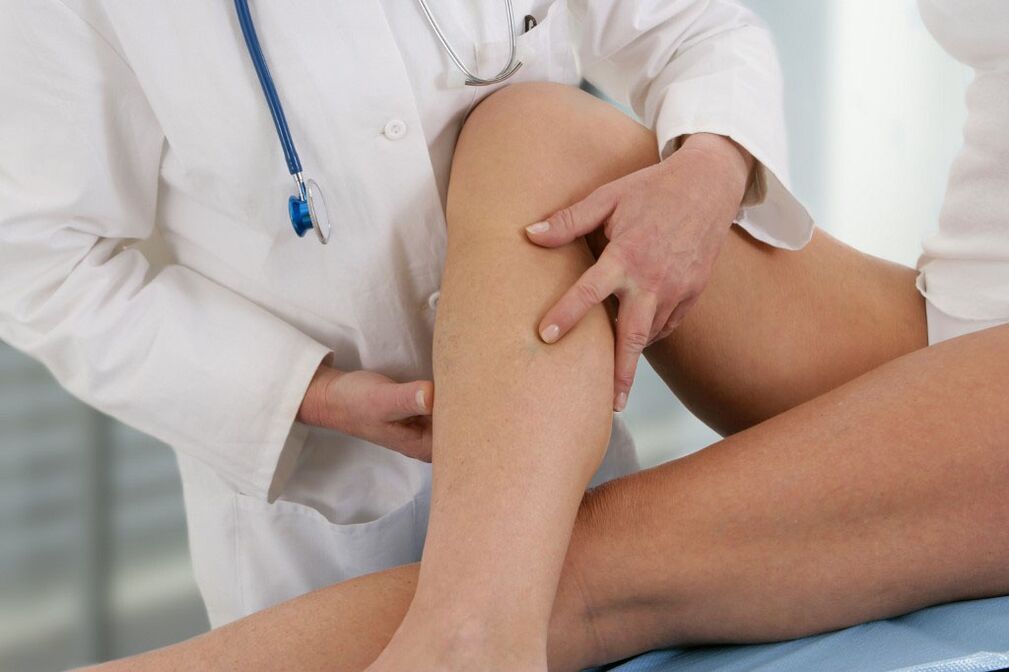
What are varicose veins?
In response to this question, many people say that the main sign of varicose veins is ugly, protruding veins. This is due to the fact that the wall of the vein expands, stretches, and the vessel loses its tone. In fact, varicose veins are the main manifestation of varicose veins, but why does this happen?
Blood flows from the bottom up through the veins. In this case, the leg muscles play the role of a kind of pump: by contracting, they "lift" the blood through the vein to the heart. But if you mostly sit and move little during the day, the muscles contract poorly and the mechanism that helps the blood flow failsblood stagnates in the vein, which creates the prerequisite for the formation of varicose veins.
The second important mechanism that ensures normal blood flow through the veins of the legs is the presence of valves in the walls of the veins. Normally, they close and prevent blood from flowing from top to bottom. If the valves weaken, reflux occurs - backflow of blood. As a result, it stagnates and stretches the vessel. With the loss of tone, the vein wall expands and the vessel can no longer fulfill its function 100%. This condition is called varicose veins.
Thus, varicose veins are the result of the weakening of the venous valves, which allow blood to flow in the opposite direction, which leads to its stagnation. Varicose veins most often affect the superficial veins of the legs. Affected veins are clearly visible under the skin and appear lumpy and tortuous.
What factors influence the development of varicose veins
The risk factors affecting the development of varicose veins can be divided into several groups:
- Long-term load on the vascular wall - this can be monotonous load (forced sitting or standing during the day), as well as heavy load associated with weight lifting (for example, among athletes).
- Hormonal imbalance that affects the condition of the venous valves. That is why pregnancy is often accompanied by varicose veins, and teenagers and young people who are actively undergoing hormonal changes are also at risk. Varicose veins also threaten women taking hormonal contraceptives.
- Heredity. The vessel wall contains so-called structural proteins - collagen and elastin. Their ratio ensures the flexibility of the vein. A person may have a congenital abnormality in the ratio of these proteins, which leads to weakness of the vein wall. This determines the innate tendency to varicose veins.
Pay attention to the following points: the presence of varicose veins in close relatives, the presence or absence of hormonal fluctuations (taking contraceptives and other hormonal drugs, pregnancy, breastfeeding), an adequate level of physical activity during the day.
Why are varicose veins dangerous?
In the absence of timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, varicose veins can cause serious complications in the later stages, such as:
- rupture of a dilated vein, followed by heavy bleeding;
- phlebitis - inflammation of the vessel wall;
- thrombophlebitis - inflammatory process of the vessel wall, on the inner surface of which a blood clot (thrombus) is formed;
- thrombosis - blockage of the lumen of the vein with blood clots, which impairs blood flow;
- thromboembolism - a condition in which a blood clot breaks away from the site of its formation and travels with the circulating blood to other structures of the body, blocking smaller vessels and causing ischemia;
- Trophic ulcers are long-lasting, non-healing wounds on the skin of the legs, resulting from impaired blood circulation and tissue trophism.
Many complications are difficult to treat, significantly reduce a person's quality of life, and lead to irreversible consequences.
Back pain: what to watch out for
So, varicose veins are one of the most common vascular pathologies. Many of us, especially office workers, are at risk. To understand when it's time to visit a phlebologist, answer a few questions:
- Are your feet swollen at the end of the day? Do you feel heaviness, pain or cramps in your legs at night?
- How much time do you spend in the same position during the day - sitting or standing?
- Have your relatives ever suffered from varicose veins?
- Are spider veins and tortuous red capillaries appearing on your legs?
If you answered yes to any of the above questions, we recommend that you consult a doctor. In a medical center specializing in the treatment of varicose veins, you can perform ultrasound diagnostics (takes about 20 minutes), which will identify varicose veins, if any, or allow you to assess the risk of their development. The phlebologist gives recommendations for effective prevention or treatment.
What to do if varicose veins appear
After the phlebologist diagnoses varicose veins, he selects treatment tactics, taking into account the stage of the disease and the severity of clinical symptoms. Therapeutic measures can combine conservative, drug and surgical techniques.
As part of conservative therapy, the following are prescribed:
- dietary nutrition to improve the rheological properties of blood, strengthen the vessel wall, prevent edema, normalize digestive processes, reduce body weight (if necessary);
- wearing compression clothing (stockings, socks or stockings) belonging to a certain compression class.
In addition, as part of a comprehensive treatment, the doctor may recommend external remedies to eliminate the signs of the disease. They are available in the form of ointments, gels, creams and can be divided into three large groups:
- phlebotonics (venotonics) - improves the tone of the walls of blood vessels, as a result of which dilated veins return to their original state;
- heparin - reduces blood viscosity, reduces the risk of blood clots, increases blood flow;
- anti-inflammatory - helps eliminate inflammation and pain.
Phlebotropic drugs are the basis of drug therapy. Such substances improve the outflow of lymphatic fluid, the microcirculation of blood, reduce the permeability of vessel walls, and increase their tone.
The gold standard for treating varicose veins is non-surgical methods. They make it possible to stop the progress of the pathological process, block the blood flow in the damaged veins, eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, and restore the aesthetics of the legs without scars and long-term rehabilitation.
The modern phlebology center uses all modern treatment methods:
- Sclerotherapy. A modern procedure for the removal of varicose veins by injection of a special substance - sclerosant. With the help of such a drug, the dilated blood vessel "sticks together", then it is disconnected from the general blood flow, and the blood begins to circulate through the healthy veins.
- Laser and radiofrequency vein removal. Both methods are similar in terms of thermal damage to the vein wall, as a result of which it "closes", turns into a scar, and then ceases. The procedures are full-fledged alternatives to classical surgeries and are carried out under ultrasound guidance. This allows healthy tissues to act only on pathological lesions. without damaging it.
- If surgery is necessary, the clinic performs gentle, minimally invasive surgeries: phlebectomy, miniphlebectomy, stripping, crossectomy. They can almost always be used, even in difficult cases.
A combined approach is often used in the treatment of varicose veins. For example, large veins are switched off from the blood stream with radiofrequency and laser treatment, and smaller superficial veins with tributaries are switched off with sclerotherapy. At the same time, conservative therapy is carried out.